In late 2019, Microsoft released a new PowerApps portal, joining canvas Microsoft and model-driven apps in the Microsoft family.
Power Apps was a long-awaited addition to the suite. While Model-driven app and Canvas made the app development easier and simple as compared to the InfoPath, they are deprived to be used to build public apps for unknown users. Introduction to the PowerApps portal bridges the gap existing for a long.
PowerApps is a high-productive development platform designed specially to build a business application. It has four major components:
Canvas apps
Now arrange the user experience of your app the way you want with Powerapps Canvas app development. You can connect it with the choice of your database of more than 200 data sources. It allows your creativity and business sense to guide how you want your applications to look.
-
Model-driven app
When you build a model-driven application, you can enhance Dataverse as much as possible to configure your forms, business rules, and process flows. Such applications automatically generate the best UI responsive across screens and sizes.
-
Portals
Microsoft portals help you create external-facing websites that allow non-organization users to sign in with a wide variety of identities, create and view data in Dataverse, or even browse content anonymously.
-
Microsoft Dataverse
Dataverse allows you to securely store and manage data within a set of standard and custom tables, and you can add columns to those tables when you need them.
How to create a mobile app using PowerApps in a quicker way?
One of the simplest ways to build a PowerApps is to start from a data source. It’s a three-part process.
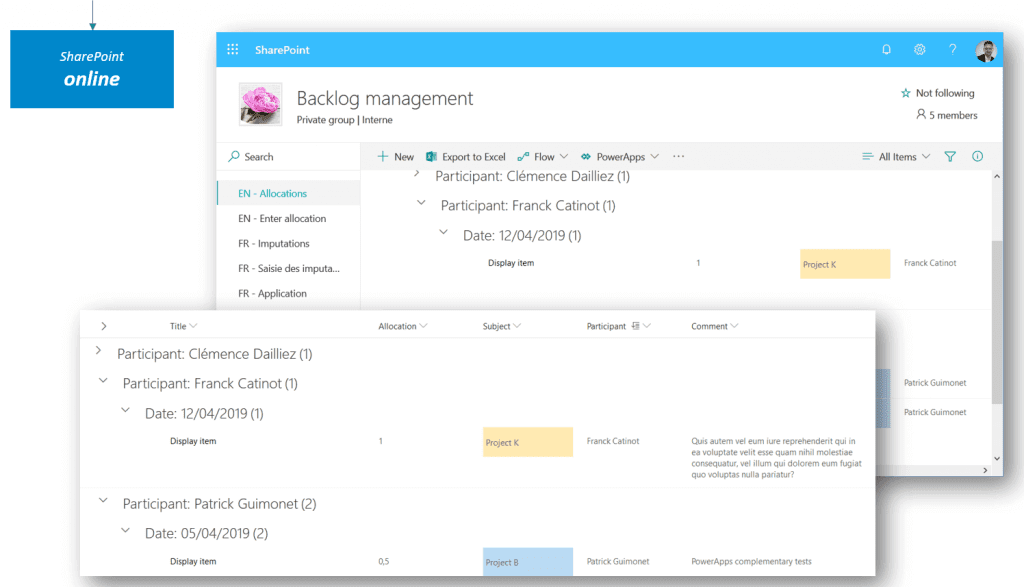
1. In this example, we’ll start with a SharePoint list that stores consulting interventions:
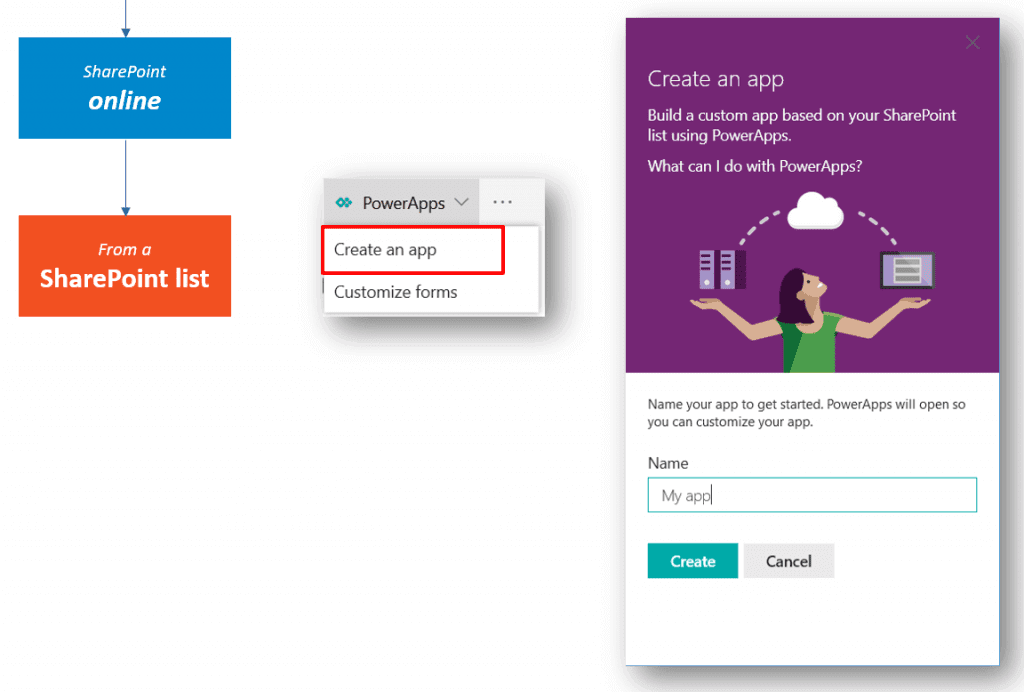
2. In the next step, we’ll select the “Create an app” option from the PowerApps menu:
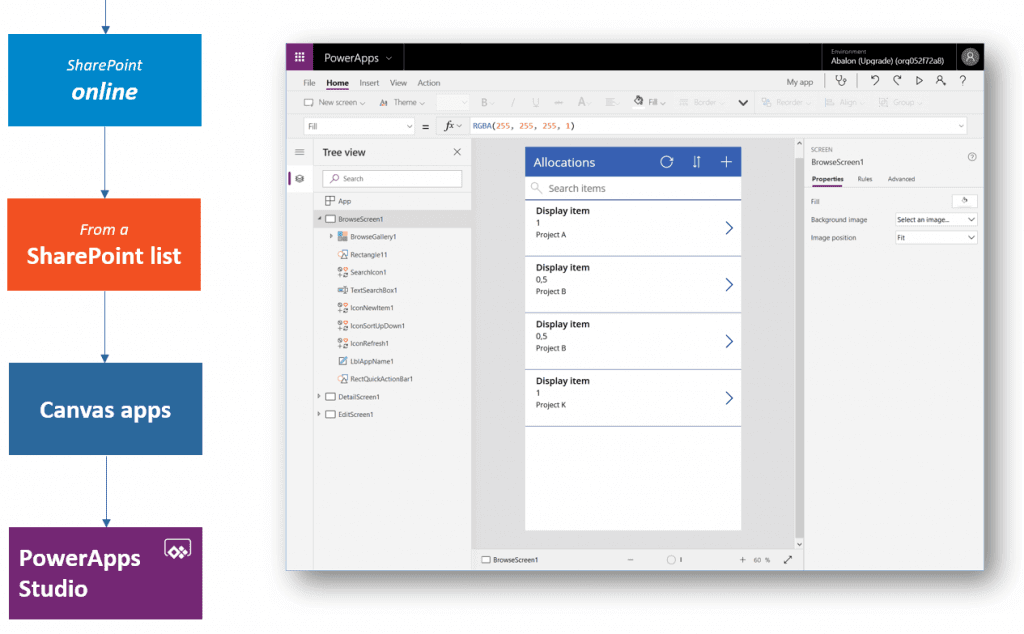
3. This step takes us to the PowerApps Studio where we will be able to find a full-functional canvas app generated by the system:
The above is just the default choices that a PowerApps developer generally prefers. There are much wider sets of available options, architectural choices, and configurations that PowerApps provide. So, without wasting much time, let’s get deep inside that.
Step 1: You need to first select your PowerApps environment
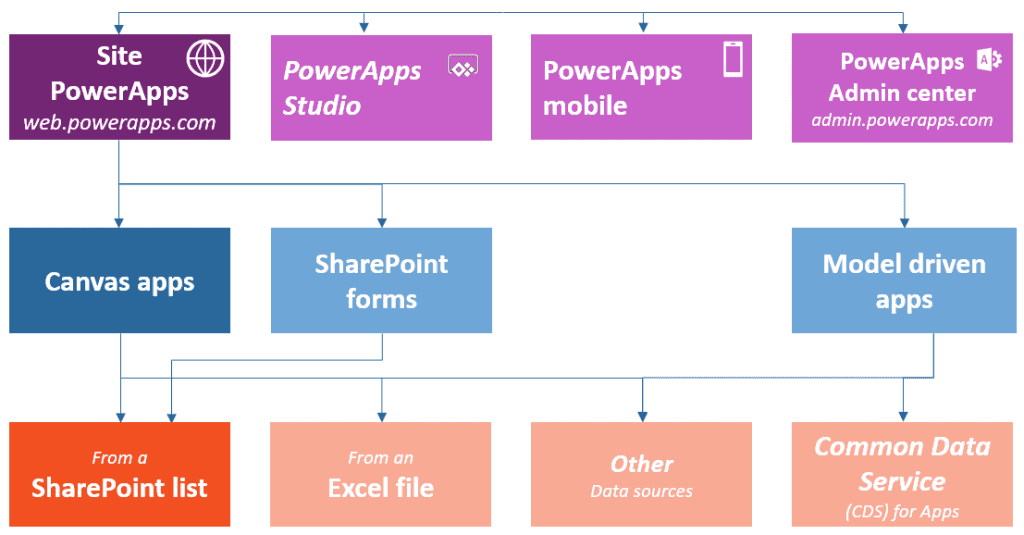
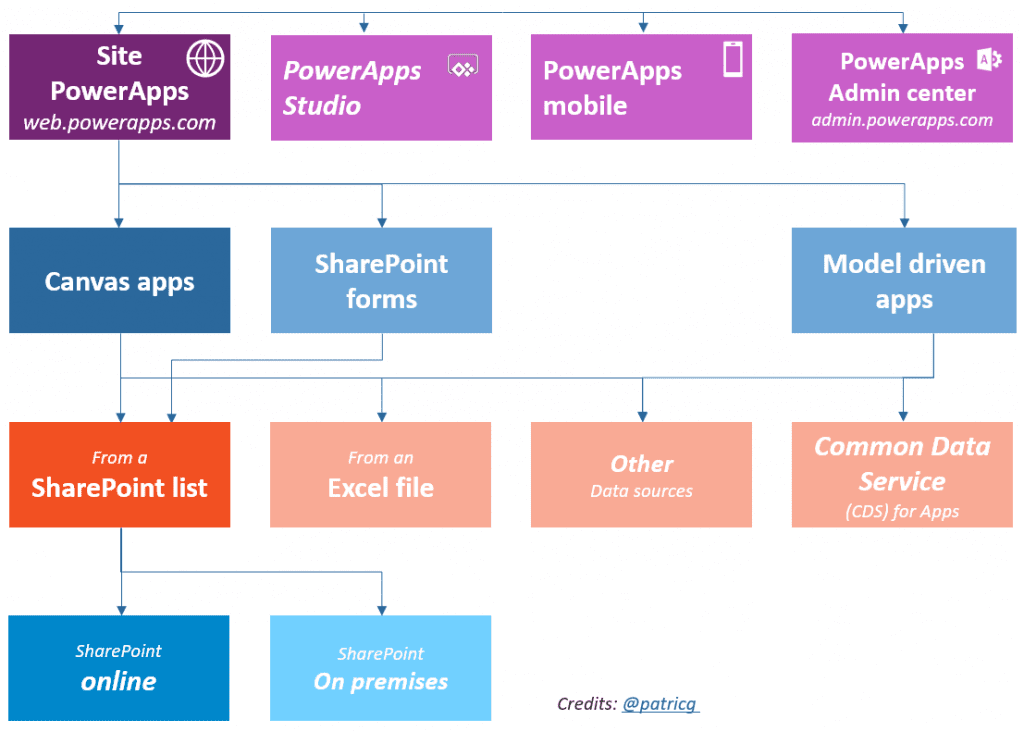
In total, there are four tools and environments in PowerApps each having its own capabilities and roles.
- Site PowerApps
- Power Apps Mobile
- Power App Admin Center
- PowerApps Studio
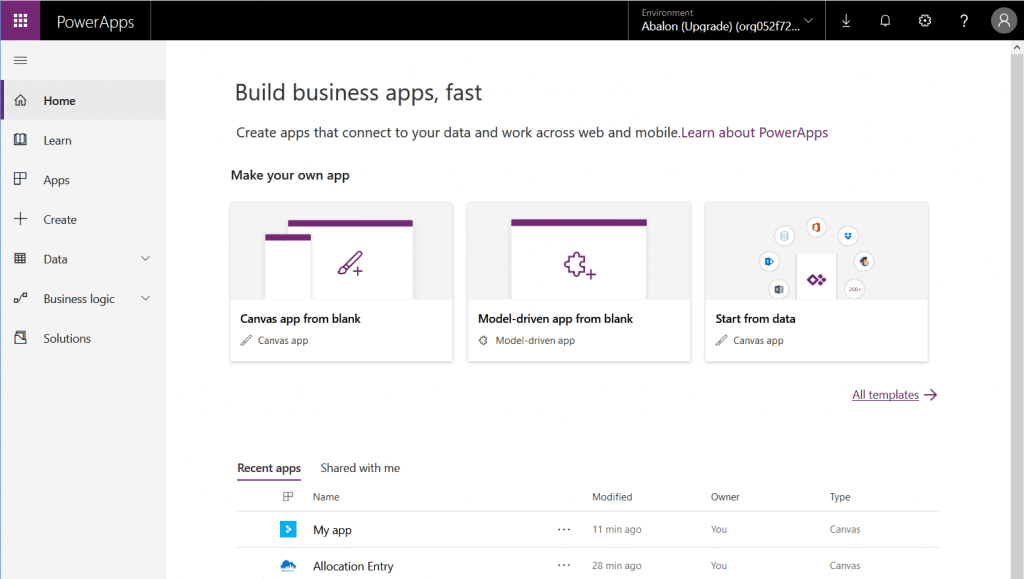
PowerApps Website
The website is the place to begin your PowerApps journey. Here, you will be able to create a new app or manage the existing ones. All you need to do is just choose the template to get started.
Power App Studio
PowerApp Studio will help you to design and adapt the applications you create as per your business needs.
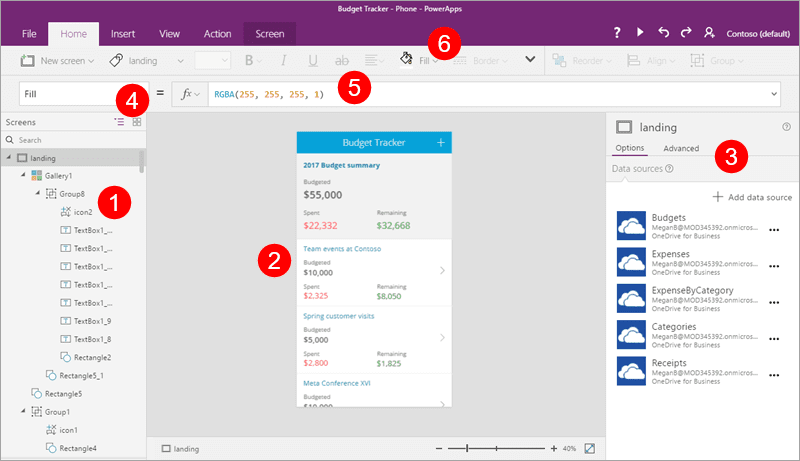
PowerApps Studio contains three panes and a ribbon that help app development quite similar as per the slide deck in PowerPoint.
PowerApps Mobile App
The mobile app developed here is available on both Android and iOS platforms along with tablets. Regardless of your platform, the application provides a runtime environment that will help you to execute all your PowerApps applications. This includes the shared ones along with the ones designed and coded from scratch.
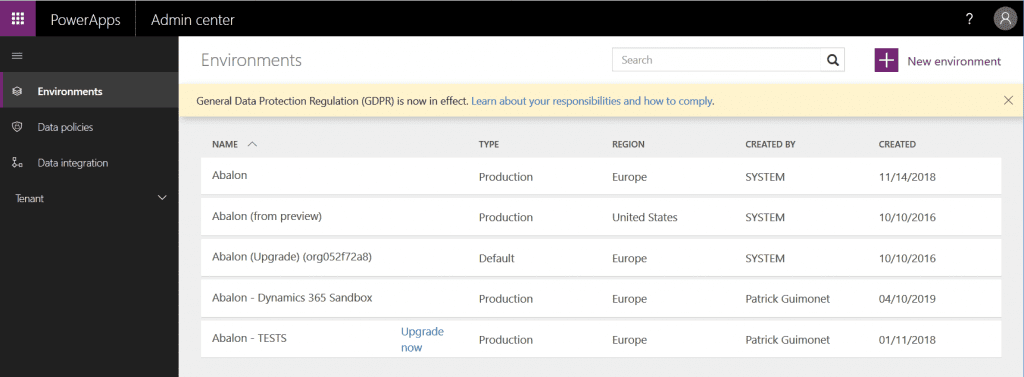
PowerApps Admin Center
It gives you the power to create and manage user roles, data loss prevention strategies, environment. You can even get lost of the user licenses in the tenant.
Step 2: Select your PowerApps application Type
There are two main types of applications you can create with PowerApps:
1. Canvas Application
Canvas app enables you to organize the interface by positioning labels and fields in a “pixel-perfect” user experience. App development focuses to bring your business knowledge and creativity to the app design. It targets lightweight apps that can be designed in minutes.
2. Model-Driven Apps
Model-driven applications are built on top of the common data services which are used to build processes, forms, and business rules. They focus on targeting heavier applications that can be used multiple times in an hour.
Step 3: Select your storage type
Power Platform especially PowerApps target innumerable interface where data is the kind and foundation of any business process. Thus, choosing appropriate data sources is highly important when it comes to designing an app.

Though share points and excel are the common grounds to be selected, apart from them, there are more than 200 data connectors available to choose from. PowerApps share connectors with the flow and logic apps where the strength of the platform is to provide connectors to the Microsoft world: SQL server, Office 365, Azure as well external data sources like Google Drive, Dropbox, and salesforce.
Just keep in mind that data source selection creates a great impact on your app licenses. If you need a premium source like Salesforce, you need to purchase P1 or P2 license.
Step 4: Connect your app to an on-premise or online data source
PowerApps is able to connect your data to the cloud and on-premise data sources. In order to connect with on-premise data sources, you need to configure an on-premises data gateway. This gateway is shared between several cloud applications like Power platform, Azure logic apps, and Azure analysis services.
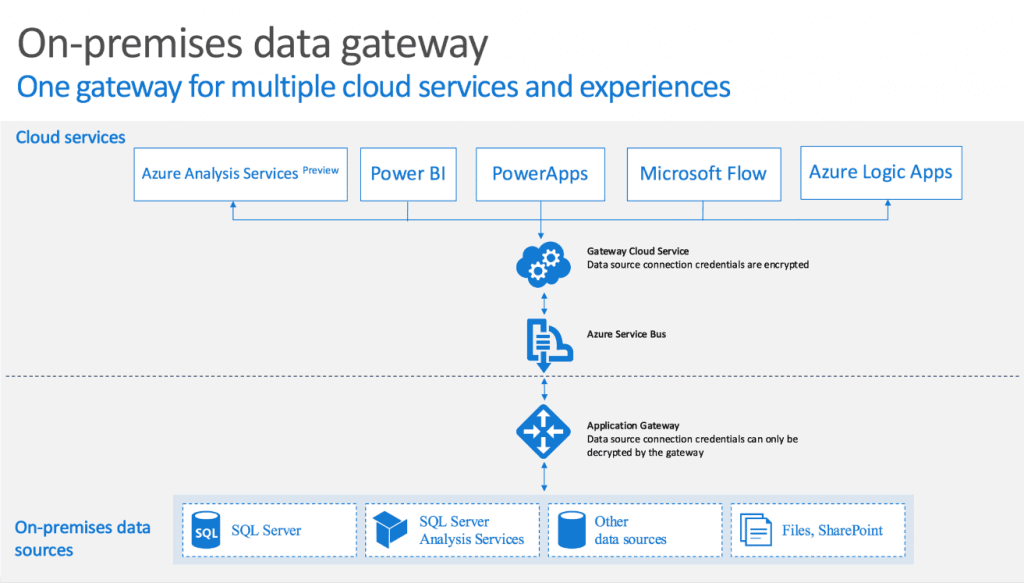
At the time of writing, supported data sources by the gateway are:
- SharePoint
- Oracle
- SQL Server
- Filesystem
- DB2
- Informix
If you are using on-premise data sources, it will have a great impact on a license to create and execute the app. If you choose a local data source, you’ll need PowerApps P1 or P2 license.
I hope the above elements will help you design better PowerApps for your business needs.
Below are few frequently asked questions about PowerApps:
1. What are PowerApps good for?
PowerApps can be used for multiple processes which involve workflow, automation, data visualization and reporting, collaboration, and more. It could involve teams, field workers, your management team, and even your customers. There can be multiple use cases ranging from simple to complex apps.
2. Is a License needed to use PowerApps?
Every PowerApps user needs a license to create or use an app. The minimum license plan a user might need is “PowerApps for office 365 and dynamics 365”.
3. What is the difference between PowerApps and Power automate?
Microsoft Power Apps is primarily an interface design tool for forms and Microsoft Power Automate is a workflow and process automation tool. They’re individual products but can also be integrated into one another.
How to Create Mobile App Using PowerApps In 10 Minutes?
Microsoft released a new PowerApps portal, joining canvas Microsoft and model-driven apps in the Microsoft family.






 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Botswana
Botswana
 USA
USA
 Italy
Italy
 Panama
Panama




 USA
USA UK
UK Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Norway
Norway India
India Australia
Australia